门面模式、代理模式、适配器
“接口隔离”模式
- 在组件构建过程中,某些接口之间直接的依赖常常会带来很多问题,甚至根本无法实现.采用添加一层间接(稳定)接口,来隔离本来相互紧密关联的接口是一种常见的解决方案.
- 典型模式:
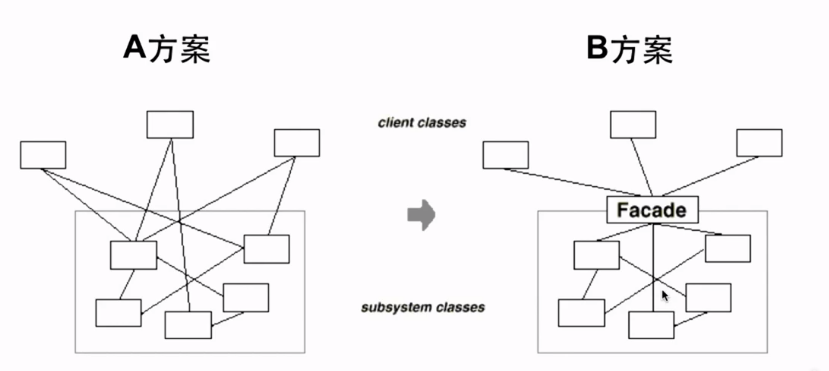
- A方案的问题在于组件的客户和组件中各种复杂的子系统有过多的耦合,随着外部客户程序和各个子系统的演化,这种过多的耦合面临着很多变化的挑战.
- 为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致(稳定)的界面,Facade模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用(复用).
代理模式
- 动机:在面向对象系统中,有些对象由于某种原因(比如对象创建的开销很大,或者某些操作需要安全控制,或者需要进程外的访问等),直接访问会给使用者,或者系统结构带来很大麻烦.
- 为其他对象提供一种代理,以控制(隔离、使用接口)对这个对象的访问
- “增加一层间接层”是软件系统中对许多复杂问题的一种常见解决方案.在面向对象系统中,直接使用某些对象对带来很多问题,作为间接层的proxy对象便是解决这一问题的常用手段.
代码例子
常规代码设计方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public interface ISubject{
pub1ic void process();
}
public class RealSubject implements ISubject{
public void process(){
//.....
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public class ClientApp{
ISubject subject;
public ClientApp(){
subject = new RealSubject;
}
public void run(){
//.....
subject.process();
//.....
}
}代理模式改造
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public interface ISubject{
pub1ic void process();
}
public class RealSubject implements ISubject{
public void process(){
//.....
}
}
1 | public class SubjectProxy implements ISubject{ |
1 | public class ClientApp{ |
适配器模式
- 动机:在软件系统中,由于应用环境的变化,常常要将”一些现存的对象”放在新的环境中应用,但是新环境要求的接口是这些线存对象所不满足的
- 将一个类的接口转换为客户需要的另外一个接口,Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12//目标接口(新接口)
public interface ITarget{
public void process();
}
//目标环境(新环境)
public class TargetLibary{
public void invoke(ITarget target){
target.process;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11//现存接口(老接口)
public interface IAdaptee{
public void foo(int data);
public int bar();
}
//现存类型
public class OldClass implements IAdaptee{
//.....
}
1 | //对象适配器 |
1 | public class ClientApp{ |